ServBay PKI (ServBay CA) Management
In modern web development, using HTTPS to ensure secure data transmission is critical—even in local development environments. ServBay comes with a built-in local Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and Certificate Authority (CA), known as ServBay CA. This CA can issue trusted SSL/TLS certificates for your local websites, helping you avoid browser warnings and allowing you to simulate production-level HTTPS connections locally.
This article provides a detailed guide on how to manage the local root certificate ServBay User CA - ECC Root generated by ServBay CA on macOS, and how to resolve certificate-related errors specific to ServBay CA.
What is ServBay CA?
ServBay CA is a certificate authority designed by ServBay specifically for local development environments. It allows you to issue several types of security certificates for the local websites (“Hosts”) configured in ServBay, including (but not limited to):
- Domain (TLS/SSL) certificates for enabling local HTTPS connections.
- Email (S/MIME) signing certificates.
- Document (PDF) signing certificates.
- Source code signing certificates.
During ServBay installation, ServBay CA is generated automatically, and its root certificate, ServBay User CA - ECC Root, is added to your macOS system Keychain and marked as trusted. This ensures that any certificate issued by it is trusted within your local environment.
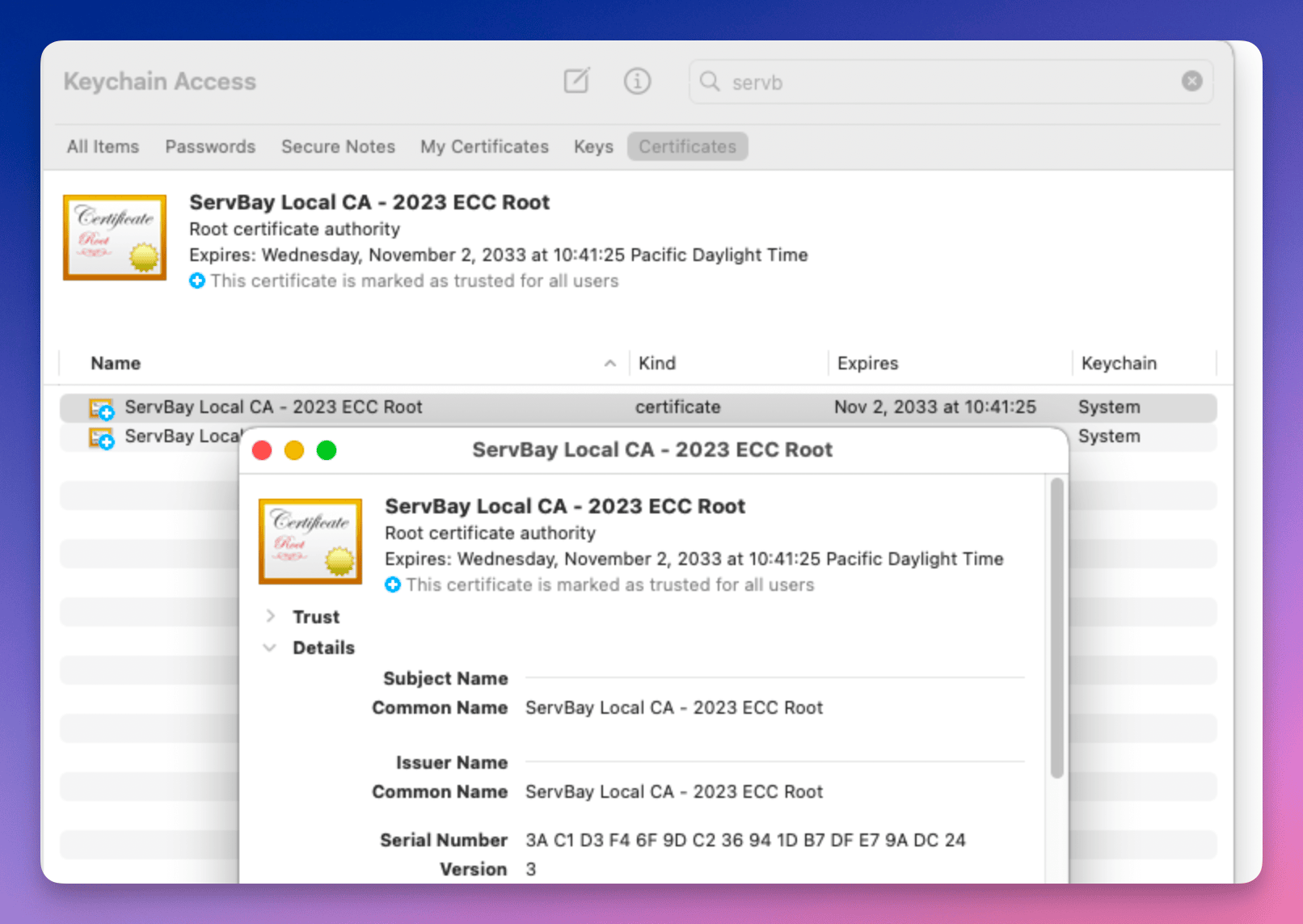 Figure 1: Certificate management interface in ServBay
Figure 1: Certificate management interface in ServBay
Requesting SSL Certificates Issued by ServBay CA
ServBay CA can issue different types of certificates to fulfill your local development needs. Refer to the following documents to learn how to request and utilize them:
- How to Request and Use a Domain Name SSL Certificate
- How to Request and Use an S/MIME Email Signing Certificate
- How to Request and Use a Document Signing Certificate
- How to Request and Use a Code Signing Certificate
Renewing SSL Certificates Issued by ServBay CA
Certificates issued by ServBay CA are valid for 800 days by default. If your certificate is about to expire or has already expired, you can renew it easily via the ServBay interface.
In the certificate management panel, locate the certificate to renew and click the refresh button (usually represented by a circular arrow) on the right side of the certificate. ServBay will issue a new 800-day valid certificate for you.
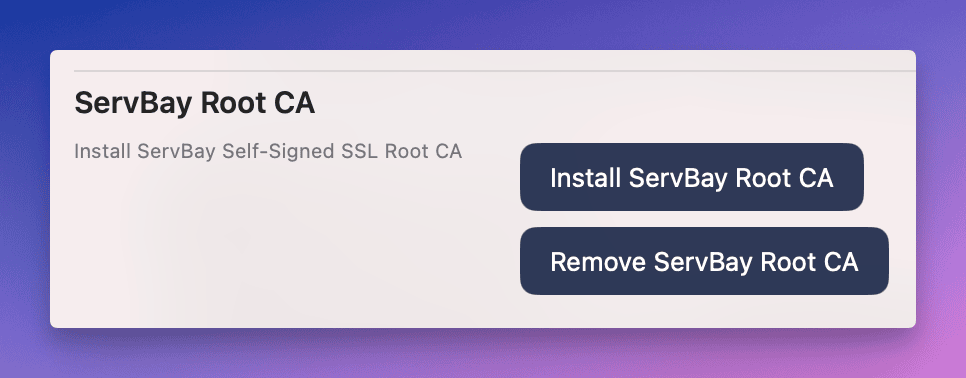 Figure 2: Certificate renewal button
Figure 2: Certificate renewal button
Exporting SSL Certificates Issued by ServBay CA
Sometimes you may need to export a certificate issued by ServBay CA, such as when using it on other devices, virtual machines, or certain applications.
In the certificate management interface, click the Export button on the right side of the certificate. ServBay will package the certificate and its private key into a .zip file for you to download.
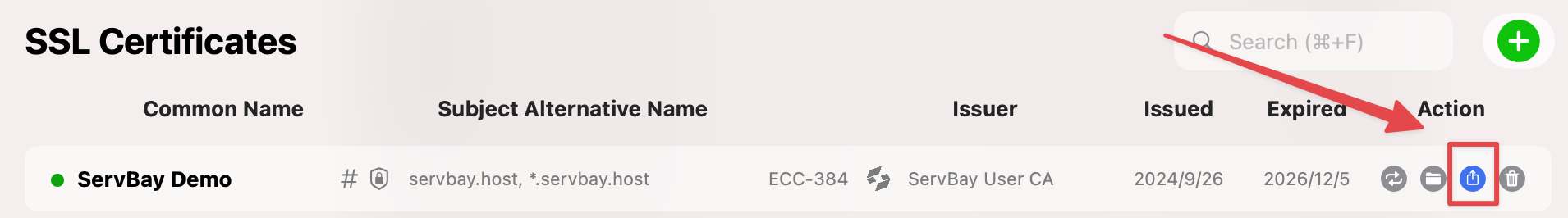 Figure 3: Export certificate button
Figure 3: Export certificate button
Deleting SSL Certificates Issued by ServBay CA
If you no longer need a particular certificate, you can delete it.
In the certificate management interface, click the Delete button on the right side of the certificate.
Note: SSL certificates that are currently in use by websites (“Hosts”) configured in ServBay cannot be deleted directly. You must first remove the website’s association with the certificate before it can be deleted.
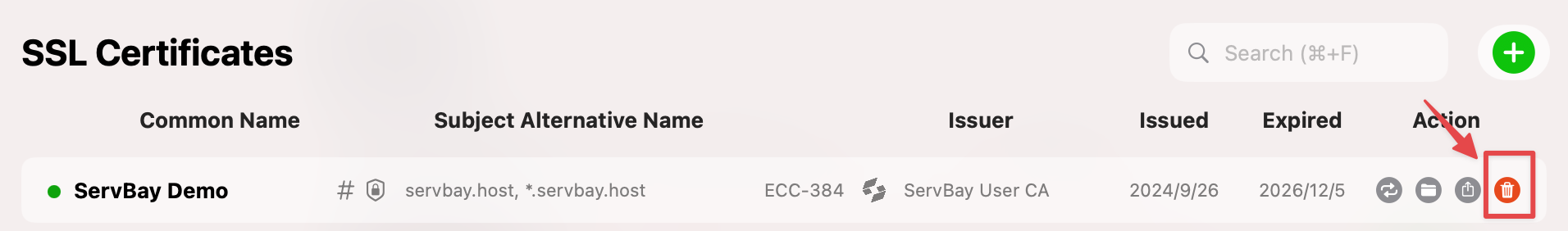 Figure 4: Delete certificate button
Figure 4: Delete certificate button
How to Find ServBay CA in macOS Keychain Access
The ServBay CA root certificate ServBay User CA - ECC Root is installed in your macOS system Keychain. You can view and manage it using the Keychain Access utility.
Step-by-step instructions:
- Open the “Keychain Access” application. You can find it quickly via Spotlight search (
Cmd + Spacethen typeKeychain Access). - In the left sidebar under the "Keychains" area, select the
Systemkeychain. ServBay CA’s root certificate is typically installed here. - In the top right search bar, enter
ServBay User CA - ECC Root. - Find the certificate in the search results. Double-click to view its details and confirm whether it is marked as “Trusted.”
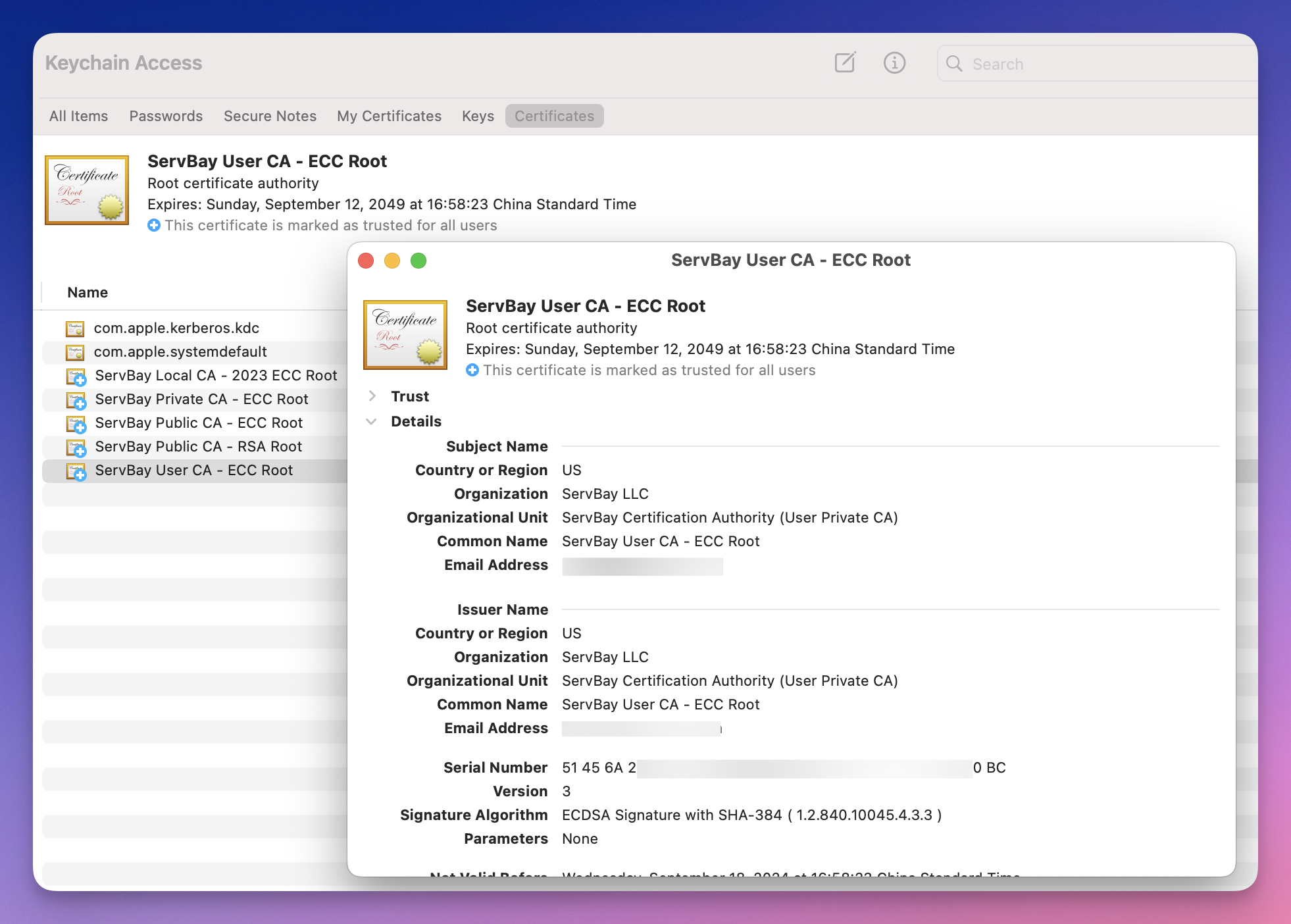 Figure 5: Finding ServBay CA in Keychain Access
Figure 5: Finding ServBay CA in Keychain Access
Resolving Local Website Certificate Error Issues
When accessing local websites configured with ServBay, if your browser displays certificate errors such as “Your connection is not private” or “NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID”, it typically means that the ServBay CA root certificate is not installed or trusted correctly by the system, or there is an issue with the website’s own certificate.
Here are some common solutions:
Reinstalling the ServBay CA Root Certificate
If the ServBay CA root certificate is missing, corrupted, or not trusted in your system Keychain, you can try reinstalling it.
- Open the ServBay application.
- Go to the ServBay management panel.
- In the management panel, navigate to the
Packagestab. - In the package list, find and click
ServBay Root CA. - Click the
Reinstall ServBay Root CAbutton. ServBay will remove any existing root certificate (if present) and reinstall theServBay User CA - ECC Rootinto the system Keychain, attempting to mark it as trusted. Enter your administrator password when prompted to complete the process.
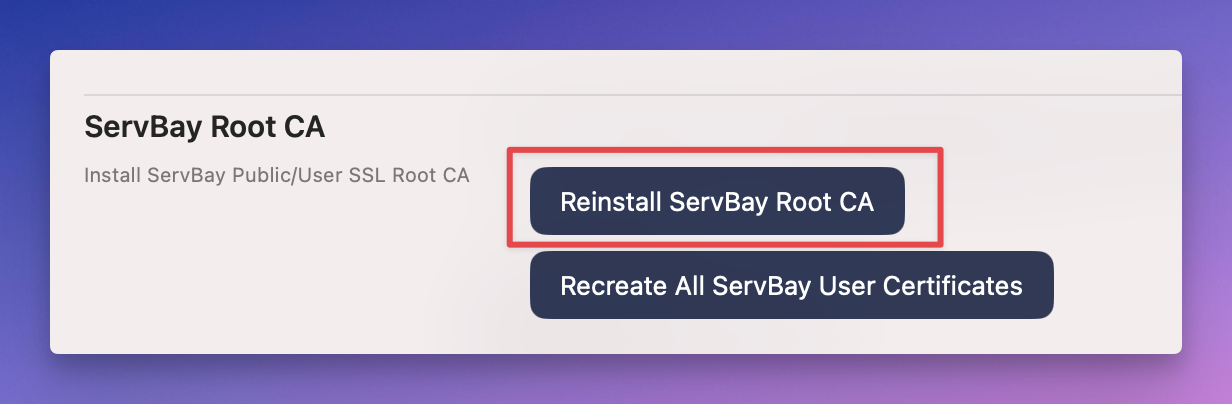 Figure 6: Reinstall ServBay Root CA
Figure 6: Reinstall ServBay Root CA
Reissuing All ServBay User Certificates
In some extreme cases—such as problems with ServBay CA itself, loss of certificate files, or certificate chain errors—you may need to reissue all certificates previously issued by ServBay CA.
In the ServBay Root CA management interface, click the Recreate All ServBay User Certificates button. This will delete all current certificates issued by ServBay CA, and generate and issue new certificates for the sites you have configured in ServBay.
Important Tip: This operation will change all local website certificates that rely on ServBay CA-issued certificates. If you have previously exported or distributed these certificates (for example, for mobile device testing), you will need to export and distribute the new certificates again to ensure uninterrupted service.
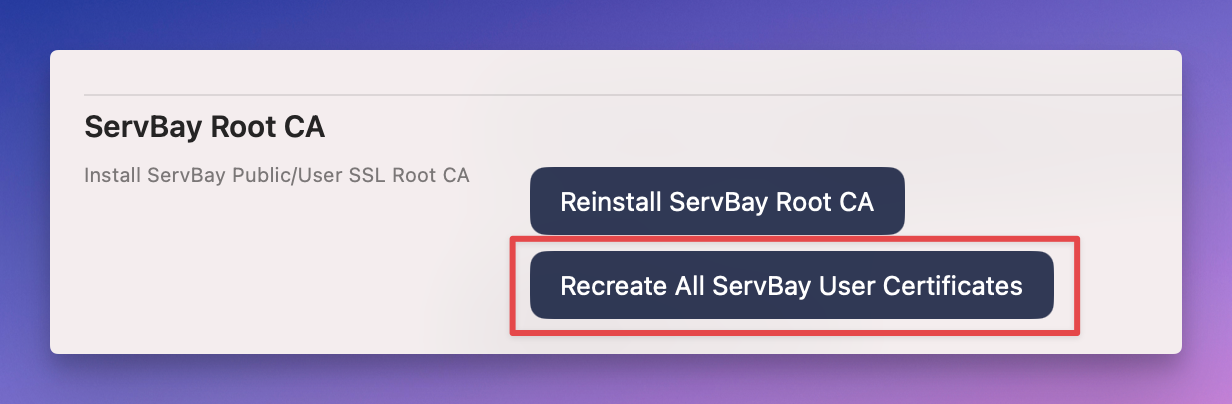 Figure 7: Reissue all ServBay User certificates
Figure 7: Reissue all ServBay User certificates
Additional Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check website configuration: Make sure your website is correctly pointed to the certificate files issued by ServBay CA.
- Browser cache: Sometimes browsers cache old certificate information. Try clearing the browser cache or visiting the site in private/incognito mode.
- System trust status: In Keychain Access, verify that the
ServBay User CA - ECC Rootcertificate is set to “Always Trust.” Double-click the certificate, expand the “Trust” section, and make sure all options are set to “Always Trust.”
Conclusion
ServBay CA is a powerful tool provided by ServBay to facilitate local web development by simplifying HTTPS configuration on macOS. With the methods described above, you can efficiently manage SSL certificates issued by ServBay CA—including requesting, renewing, exporting, and deleting them—while troubleshooting and resolving certificate errors when they occur. Proper configuration and management of ServBay CA will help you establish a more secure and production-like local development workflow.

