Managing and Using MariaDB Databases in ServBay
MariaDB is a popular open-source relational database management system, derived from MySQL, renowned for its high performance, reliability, and scalability. ServBay, as a local web development environment supporting both macOS and Windows, integrates MariaDB database services and provides developers with convenient tools for database management. This document is a comprehensive guide covering how to install, configure, connect, manage (including backup and restore), optimize, and secure your MariaDB databases within ServBay.
Installing and Configuring MariaDB
Installing MariaDB in ServBay is straightforward. Open the ServBay main interface and click on Packages in the left sidebar, then select MariaDB. Here you can view a list of available MariaDB versions. ServBay currently supports multiple versions from MariaDB 10.4 up to MariaDB 11.7.
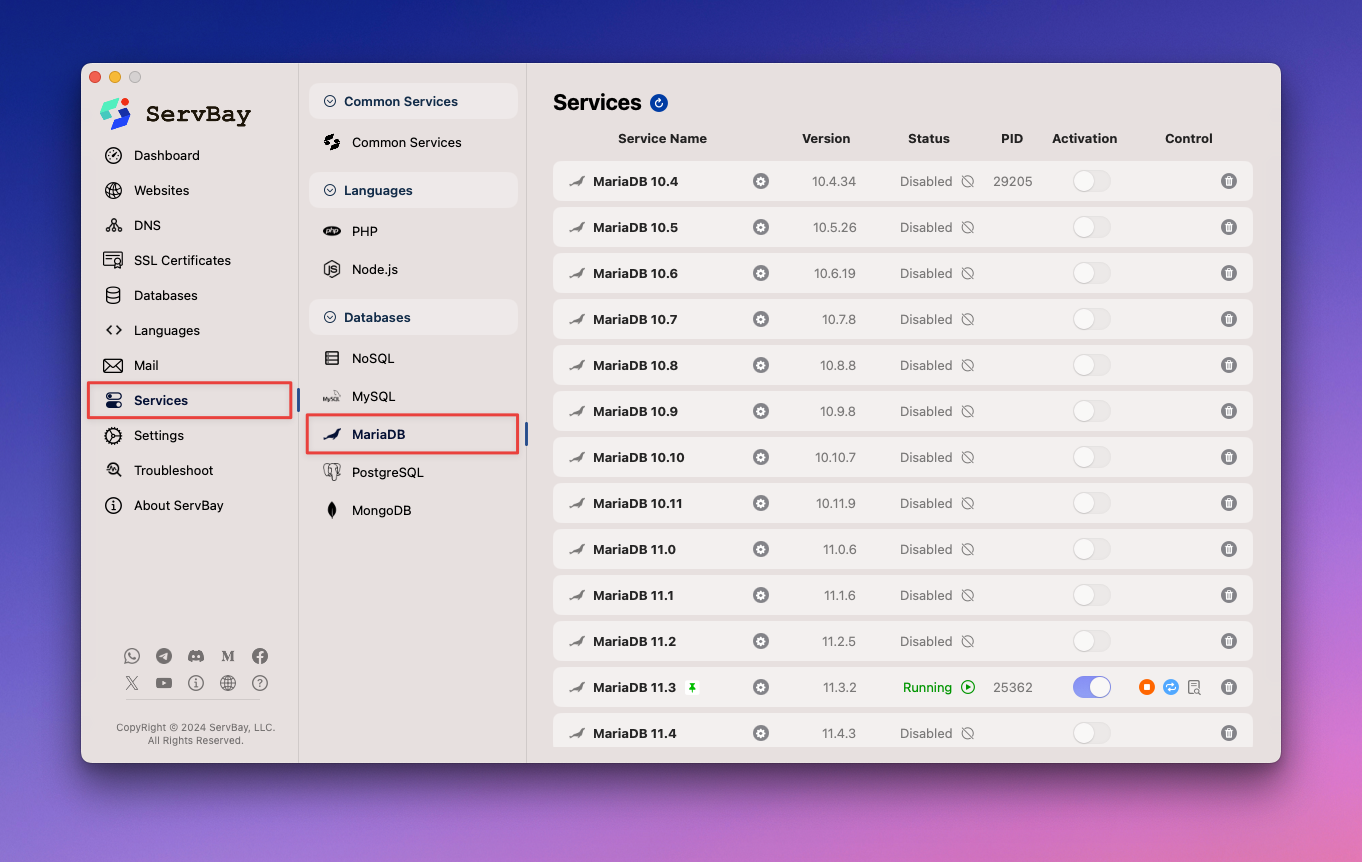
After choosing your desired MariaDB version, simply click the install button to complete the installation.
Starting and Managing MariaDB Services
Once installed, you can start, stop, or restart the MariaDB service using either the ServBay management platform or the command-line tool servbayctl.
Using the ServBay Management Platform
- Open the ServBay main interface.
- Navigate to the Packages section in the left sidebar and select MariaDB.
- In the details page for the MariaDB package, locate your installed MariaDB version.
- Use the corresponding buttons to start, stop, or restart the service.
Using the servbayctl Command-Line Tool
servbayctl is a powerful command-line utility provided by ServBay to manage its services and packages.
bash
# Start the specified MariaDB service version (e.g., MariaDB 11.3)
servbayctl start mariadb 11.3
# Stop the specified MariaDB service version
servbayctl stop mariadb 11.3
# Restart the specified MariaDB service version
servbayctl restart mariadb 11.3
# Check the status of the MariaDB service
servbayctl status mariadb 11.31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Replace 11.3 in the commands with the actual version of MariaDB that you have installed and are using.
Configuring MariaDB
ServBay offers a user-friendly graphical interface for modifying MariaDB configuration parameters and also supports direct editing of configuration files. With ServBay’s GUI, you can easily tune critical settings such as memory, cache, and connection limits to optimize MariaDB’s performance.
For detailed steps on modifying and tuning MariaDB configurations, refer to ServBay's advanced settings documentation: Modifying MariaDB Settings.
Connecting to MariaDB
MariaDB running within ServBay can be connected to in multiple ways by default, including via command-line clients or graphical management tools.
Connecting via Command Line
You can use the standard mysql command-line client to connect to the MariaDB service.
Connect via TCP/IP: Specify the hostname (
localhost) and port (default: 3306).bashmysql -u your_username -p -h localhost -P 33061After entering the command, you'll be prompted for your password. Replace
your_usernamewith your actual database username.Connect via Socket: Specify the path to the Unix domain socket file, which is typically faster than TCP/IP connection.
bashmysql -u your_username -p -S /Applications/ServBay/tmp/mysql.sock1By default, ServBay places MariaDB’s socket file at
/Applications/ServBay/tmp/mysql.sock.
Connecting via phpMyAdmin and Adminer
ServBay comes with phpMyAdmin and Adminer integrated by default, giving you easy access to graphical database management via the web.
You can access their entry pages through your browser at ServBay's local service address:
- Access URL: https://servbay.host
On this page, you'll find links to phpMyAdmin and Adminer. Click the respective link to bring up the login page. For login credentials, use the database username and password retrievable from the MariaDB package details page in the ServBay management interface.
Database Management
Creating Databases and Users
Once connected to MariaDB, you can execute SQL commands to create new databases and manage user permissions.
Create a Database:
sqlCREATE DATABASE mydatabase_servbay;1It's recommended to use descriptive database names, such as
mydatabase_servbay.Create a User and Grant Permissions: Create a dedicated database user for your application or project, granting only the necessary permissions as a good security practice.
sql-- Create a new user, e.g., servbay-demo with a specified password CREATE USER 'servbay-demo'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'a_strong_password'; -- Grant all privileges on a specific database to the user GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON mydatabase_servbay.* TO 'servbay-demo'@'localhost'; -- Refresh privileges to apply changes immediately FLUSH PRIVILEGES;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8Replace
servbay-demoanda_strong_passwordwith your desired username and a strong password, and replacemydatabase_servbaywith your created database name.@'localhost'restricts the user to local connections only.
Backup and Restore
Regular backups are essential for data security. In the ServBay environment, you can manually perform backups using command-line tools or make use of ServBay’s automatic backup feature.
Manual Database Backup
Use the mysqldump tool to export your database as an SQL file. It’s recommended to store the backup file in ServBay’s backup directory:
bash
/Applications/ServBay/backup/mariadb1
Execute the backup command:
bash
mysqldump -u servbay-demo -p mydatabase_servbay > /Applications/ServBay/backup/mariadb/mydatabase_servbay_backup.sql1
Replace servbay-demo and mydatabase_servbay with your username and database name. You'll be prompted for your password after running the command.
Manual Database Restore
Use the mysql tool to import the SQL backup file into your database.
bash
mysql -u servbay-demo -p mydatabase_servbay < /Applications/ServBay/backup/mariadb/mydatabase_servbay_backup.sql1
This will restore the data in /Applications/ServBay/backup/mariadb/mydatabase_servbay_backup.sql to the mydatabase_servbay database.
ServBay Automatic Backup Feature
ServBay provides a powerful automatic backup feature for periodic backup of MariaDB databases, website files, ServBay configs, SSL certificates, and other vital data. You can configure the backup frequency, retention count, and storage location in ServBay’s settings. This feature greatly simplifies your backup workflow and ensures data safety. For detailed instructions, see How to Automatically Back Up and Restore MariaDB Databases.
Performance Optimization
MariaDB offers various performance optimization options; here are some common methods suited for local development and testing in the ServBay environment.
Index Optimization
Creating indexes on columns frequently used in WHERE clauses, JOIN conditions, or ORDER BY statements can significantly boost query speed.
sql
-- Create an index on column_name in your_table_name
CREATE INDEX idx_column_name ON your_table_name(column_name);1
2
2
Query Optimization
Use the EXPLAIN command to analyze the execution plan of SQL queries. This helps you see how the query reads data, whether indexes are used, and where improvements can be made.
sql
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM your_table_name WHERE column_name = 'value';1
Based on the output of EXPLAIN, consider rewriting your query, adding indexes, or changing the table structure.
Configuration Tuning
Tweaking MariaDB’s configuration files (usually my.cnf or my.ini), focusing on memory usage, cache, and concurrent connections, can further improve performance. One of the most important parameters is innodb_buffer_pool_size, which determines how much memory InnoDB uses for caching data and indexes. Adjust it according to your hardware’s RAM size.
ini
[mysqld]
# Adjust InnoDB buffer pool size, e.g., 50–70% of physical memory
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 1G1
2
3
2
3
After making configuration changes, restart the MariaDB service for them to take effect. You can do this via the ServBay GUI or the servbayctl restart mariadb <version> command.
Security Management
Database security should be a priority, even in local development environments, as it helps you build good security habits.
Set Strong Passwords
Assign complex and unique passwords to all database users, especially the root user. Avoid weak or default passwords.
sql
-- Change a user's password
ALTER USER 'servbay-demo'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'a_new_strong_password';
-- Or use old syntax (depending on MariaDB version)
SET PASSWORD FOR 'servbay-demo'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('a_new_strong_password');1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
Regular Backups
As discussed above, regular backups are essential to prevent data loss. Combine manual backups with ServBay’s automatic backup feature for timely and reliable protection.
Restrict Access
Follow the principle of least privilege, granting users only the minimum permissions needed for their tasks. Avoid granting global privileges (like ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.*) to application users.
sql
-- Revoke all privileges on all databases from a user (use with caution)
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* FROM 'servbay-demo'@'localhost';
-- Grant only SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE on a specific database
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE ON mydatabase_servbay.* TO 'servbay-demo'@'localhost';
-- Refresh privileges
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Unable to Connect to MariaDB
If you are unable to connect to MariaDB, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Check if MariaDB service is running: Use the ServBay GUI to check the MariaDB package status or the
servbayctlcommand:bashIf the service isn’t running, try starting it.servbayctl status mariadb <version>1 - Verify connection parameters: Ensure you're using the correct username, password, hostname (
localhost), port (3306), or socket path (/Applications/ServBay/tmp/mysql.sock). - Check firewall settings: Make sure your macOS firewall isn’t blocking ServBay or MariaDB processes. This is usually not an issue locally, but should be considered when enabling remote connections.
Wrong Password
If you’re receiving password errors when connecting to MariaDB or have forgotten the root password, refer to the ServBay documentation for password reset instructions:
ServBay makes it easy to reset root passwords for MariaDB, MySQL, and PostgreSQL databases.
Permission Issues
If you can connect to the database but cannot perform certain actions (such as creating tables or inserting data), your user account may lack adequate permissions.
- Check current user permissions:sqlReplace
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'your_username'@'localhost';1your_usernamewith the username you're currently using. - Grant necessary permissions as needed: If privileges are insufficient, log in as a user with higher rights (like root), grant needed permissions, and then refresh.sql
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON mydatabase_servbay.* TO 'servbay-demo'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;1
2
Conclusion
MariaDB is a core and powerful component in the ServBay local development environment. With ServBay’s convenient management interface and utilities, you can efficiently install, configure, connect to, manage, optimize, and secure your MariaDB databases. Mastering these basic operations is crucial for building stable, high-performance web applications. We hope this article helps you get the most out of MariaDB in ServBay, providing solid data support for your local development workflow.

