ServBay PHP Version Management: CLI and Website Environment Configuration Guide
ServBay is a robust local web development environment for macOS and Windows, supporting multiple programming languages and databases. This article explains how to flexibly manage different PHP versions for various projects in ServBay, whether executing scripts via the command line, or serving specific websites. Mastering PHP version management in ServBay can significantly boost your development efficiency by ensuring environment isolation and project stability.
1. Command Line Environment: Using .servbay.config for Project-Level PHP Version Control
By creating a .servbay.config configuration file in the project root directory, developers can define an independent PHP version for each project in the command-line environment. ServBay automatically loads the corresponding PHP environment based on your current terminal directory, achieving project-based version isolation and avoiding global config conflicts.
1. Purpose and Principles of .servbay.config
- Project-Level Version Control: ServBay enables simultaneous installation and operation of multiple PHP versions, from PHP 5.6 to the latest stable and development releases. With
.servbay.config, you can precisely specify the required PHP version for each project. - Seamless Switching: When you use the
cdcommand to enter a directory containing a.servbay.configfile, ServBay automatically detects it and temporarily adjusts environment variables (primarilyPATH) for the current terminal session. This ensures that commands likephpandcomposerpoint to the configured PHP executable. When you leave the directory, the environment reverts to ServBay's global defaults, with no side effects on the system.
2. Configuration Steps
Create a file named .servbay.config in your project root directory, and add contents as follows to specify the PHP version:
bash
# Specify the PHP version to use for this project (e.g., PHP 8.3)
PHP_VERSION=8.3
# If your project also requires a specific Node.js version, specify it too (e.g., Node.js 20)
# NODE_VERSION=201
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
- The value of
PHP_VERSIONshould correspond to a PHP version identifier installed in ServBay, typically in the format of major or major-minor version numbers (such as7.4,8.1,8.3,8.5). Double-check that the specified version is installed and enabled in ServBay. - The
NODE_VERSIONsetting works similarly to designate the Node.js version for your project if needed.
Verifying the Configuration:
Open a terminal in the directory containing .servbay.config, then run:
bash
$ pwd # Confirm you are in the project root directory
$ php -v # Check if the output matches your specified PHP version (e.g., PHP 8.3.x)
$ composer install # Dependency resolution and installation will use the currently active PHP version1
2
3
2
3
If you update .servbay.config and the version doesn't switch, try closing and reopening the terminal, or use cd . to force ServBay to reload the configuration.
3. Tips and Advanced Usage
- Version Compatibility: If you encounter errors like "Class not found" or "Call to undefined function," first review your project's dependencies (such as the
composer.jsonPHP version requirement) and make sure the selected PHP version meets those constraints. Some legacy projects may rely on features or extensions removed in newer PHP releases (for example, PHP 7.2 dropped themcryptextension). - Global Default Behavior: If there is no
.servbay.configfile in your current directory or any parent directories, ServBay uses the PHP version set in its graphical “Settings” interface as the global default. - Multi-Service Support:
.servbay.configcan also define the Node.js version (viaNODE_VERSION). This is especially useful for projects using PHP for the backend and Node.js as a frontend build tool (like Webpack or Vite).
4. Usage Demonstration
Here's a sample demonstration of how .servbay.config enables automatic PHP version switching in different project directories:
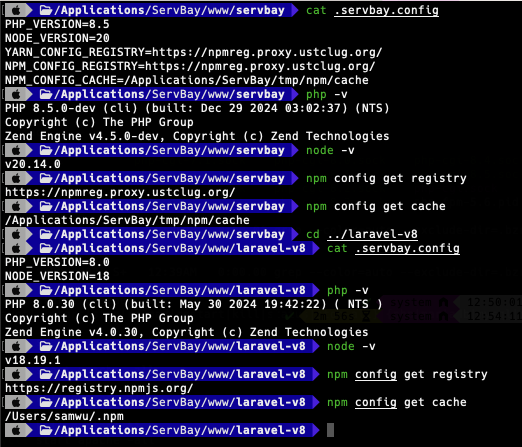 Image description: In ServBay, entering directories with different
Image description: In ServBay, entering directories with different .servbay.config files and running php -v switches the terminal to the PHP version specified in each file automatically.
2. Website Environment: Managing PHP Versions via ServBay GUI
ServBay’s graphical interface offers a user-friendly way to configure an independent PHP version for each website. The website PHP environment is completely separate from the CLI environment, allowing you to choose versions based on actual site requirements.
1. Configuration Steps
- Launch ServBay GUI: Start the ServBay application.
- Access Website Management: Click the Websites tab on the left navigation bar of the main interface.
- Add or Edit a Website:
- Click the + button in the lower left to add a new website configuration.
- Edit an existing website by selecting it.
- Configure Site Properties:
- Root Directory: Set the directory containing your website files. It’s recommended to use a subdirectory under ServBay’s default website location
/Applications/ServBay/www/, for example,/Applications/ServBay/www/your-website-name/public(common for Laravel or Symfony projects). - Domain: Specify the local dev domain you’ll use, such as
your-website-name.servbay.demo. ServBay automatically sets up local DNS and HTTPS certificates for these domains (using ServBay User CA or ServBay Public CA), making development and testing easier. - PHP Version: Select your preferred PHP version from the dropdown menu. ServBay lists all installed and enabled PHP versions (e.g., 7.4, 8.1, 8.3, 8.5).
- Root Directory: Set the directory containing your website files. It’s recommended to use a subdirectory under ServBay’s default website location
- Save Configuration: Click the save button when finished. ServBay applies the changes and may reload or restart the web server and PHP-FPM process as needed.
2. Technical Details and Benefits
- Service Isolation: Each site's PHP version is typically run via a separate PHP-FPM process pool. This ensures complete isolation between sites—errors or memory leaks on one site won’t affect others.
- Performance Optimization: ServBay packages (including all PHP versions) are tuned for ARM64 (Apple Silicon) and X86_64 architectures, delivering optimized performance on different hardware.
- Error Diagnostics:
- Check PHP error logs: Website PHP errors are usually logged in
/Applications/ServBay/var/log/php/php_error.log. - Check PHP-FPM process status: Use ServBay’s CLI tool
servbayctlto view the status of a specific PHP version, for example,servbayctl status php 8.3.
- Check PHP error logs: Website PHP errors are usually logged in
3. Web Server and Database Integration
ServBay is highly flexible, letting you choose the web server and database to best suit each project:
- Web Server Support: As of ServBay 1.7.0 and above, you can easily switch website servers between Apache, Nginx, and Caddy. These seamlessly integrate with ServBay-managed PHP-FPM processes.
- Database Integration: ServBay lets you install and manage multiple versions of MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Redis. You can connect your website, or your project code, to the desired database instance running within ServBay—ideal for projects needing specific database versions or types (e.g., some Laravel projects work best with MariaDB 11.x).
3. Cross-Environment Coordination and Best Practices
Understanding the independence and configuration methods of CLI and website PHP version management empowers you to make optimal choices in different development scenarios:
| Scenario | CLI Environment (.servbay.config) | Website Environment (ServBay GUI) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maintaining legacy systems | Set PHP_VERSION=5.6 in project root | Select PHP 5.6 in website configuration | Ensure required PHP version and extensions are installed in ServBay. |
| New project development (e.g. Laravel 11) | Set PHP_VERSION=8.3 (or higher), optionally NODE_VERSION=20 | Add site, set root to project’s public, choose PHP 8.3+, set dev domain & HTTPS | Keep CLI tools (Composer, Artisan, Node builders) and web PHP version consistent. |
| Testing future PHP releases | Set PHP_VERSION=8.5 in test project root | Add testing site, select PHP 8.5 | Use this for compatibility checks with the latest PHP. |
| Running Composer commands | Ensure correct PHP_VERSION in current or parent .servbay.config | N/A (Composer runs in CLI) | Composer uses the currently active PHP version in the terminal. |
Notes
- Differences Between CLI and Web Environments: Even if PHP shares the same version number in both CLI and web (PHP-FPM) environments, their default configs and loaded extensions may differ. For instance,
opcacheis usually enabled by default in PHP-FPM for performance, but disabled in CLI mode. If you experience behavioral differences, check the respectivephp.inifiles (ServBay maintains separate ones for each PHP version) and the loaded extensions. - Keeping ServBay Runtime Updated: Make sure ServBay and its runtime are always up to date. The ServBay team continuously updates packages, including new PHP versions and security fixes. Generally, updating ServBay will also update the runtime, bringing the latest features and improvements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What should I do about PHP version conflicts between CLI and website environments?
A: The command line environment (controlled by .servbay.config) and website environment (controlled via the ServBay GUI) are completely separate. .servbay.config only affects which PHP version the php command points to in your current terminal session. The website configuration determines which PHP version the web server (Apache/Nginx/Caddy) invokes via PHP-FPM for web requests. There’s no direct conflict between the two. You can use different PHP versions for CLI (like Composer or Artisan) and your site, but for best results—and to match production—it’s recommended to use the same PHP version in both environments.
Conclusion
ServBay empowers developers with robust and flexible PHP version management via the .servbay.config file and an intuitive graphical interface. Whether you’re maintaining legacy projects on older PHP versions or building new applications with the latest releases, ServBay makes it easy to handle diverse requirements. Leveraging these features helps bring your local dev environment closer to production, improving both workflow efficiency and project stability.

