ServBay Web Server Troubleshooting Guide
ServBay supports using Caddy, NGINX, and Apache as default web servers, giving you a flexible local development environment. During use, you may encounter issues such as your site being inaccessible, slow to load, or returning errors like 500 Internal Server Error. This guide will help you diagnose and resolve common web server problems in your ServBay setup.
Using ServBay’s Built-in Troubleshooting Tool
ServBay offers a powerful built-in Troubleshooting Tool that automatically detects common configuration and service issues and provides helpful prompts. We highly recommend using this tool for self-diagnosis when problems arise.
Open the ServBay application and click Troubleshooting in the left navigation to access ServBay’s built-in diagnostic interface.
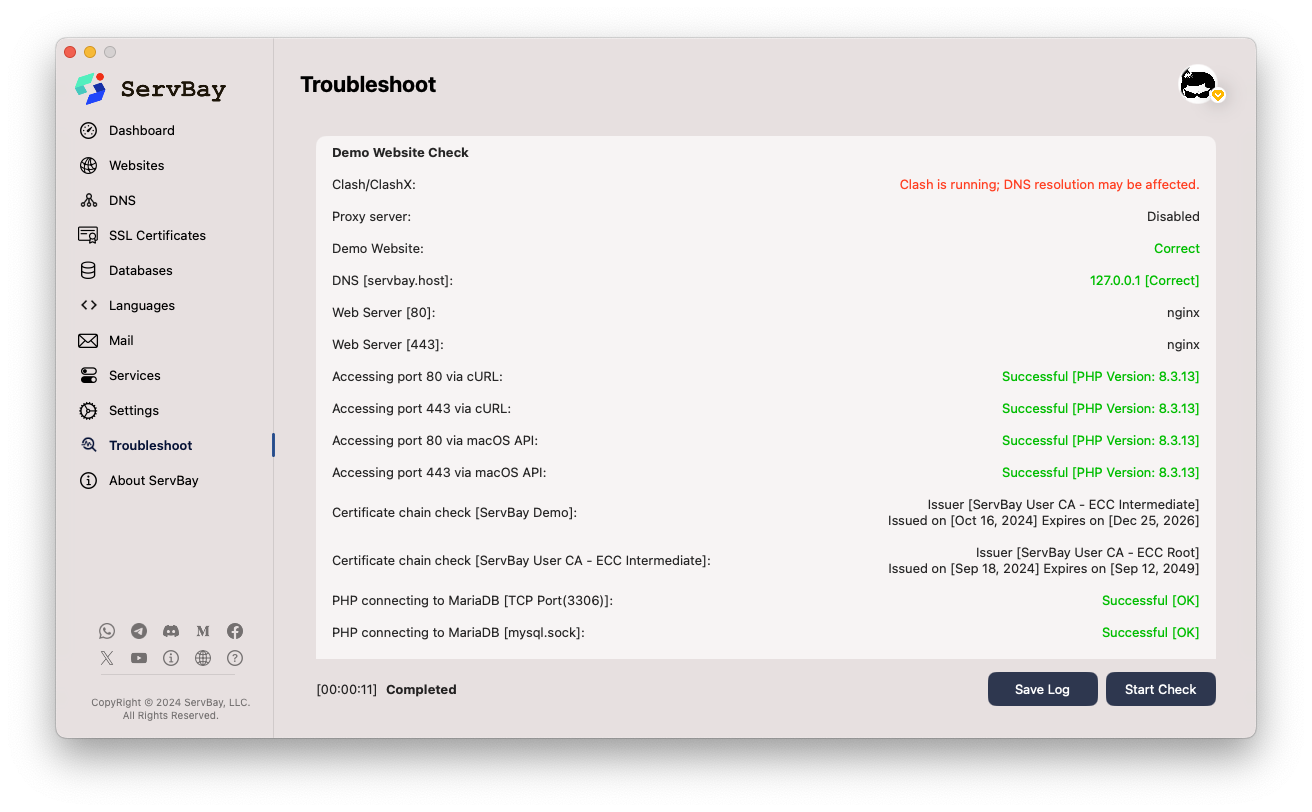
The tool checks the status of ServBay’s core components, port occupancy, configuration syntax, and more, offering relevant tips and suggestions to help you quickly pinpoint the issue.
Slow First Website Visit After Migrating from MAMP or Laravel Herd
If you switched from MAMP or Laravel Herd to ServBay and notice that the first visit to your website after idle periods takes over 5 seconds to load, though subsequent visits are fast for a while—then becomes slow again after another idle period—read on.
Problem Symptoms
Open Chrome Developer Tools (F12 or Cmd+Option+I), go to the Network tab, refresh your page, and click the request for detailed Timing info. You’ll see the DNS Lookup step taking around 5 seconds.
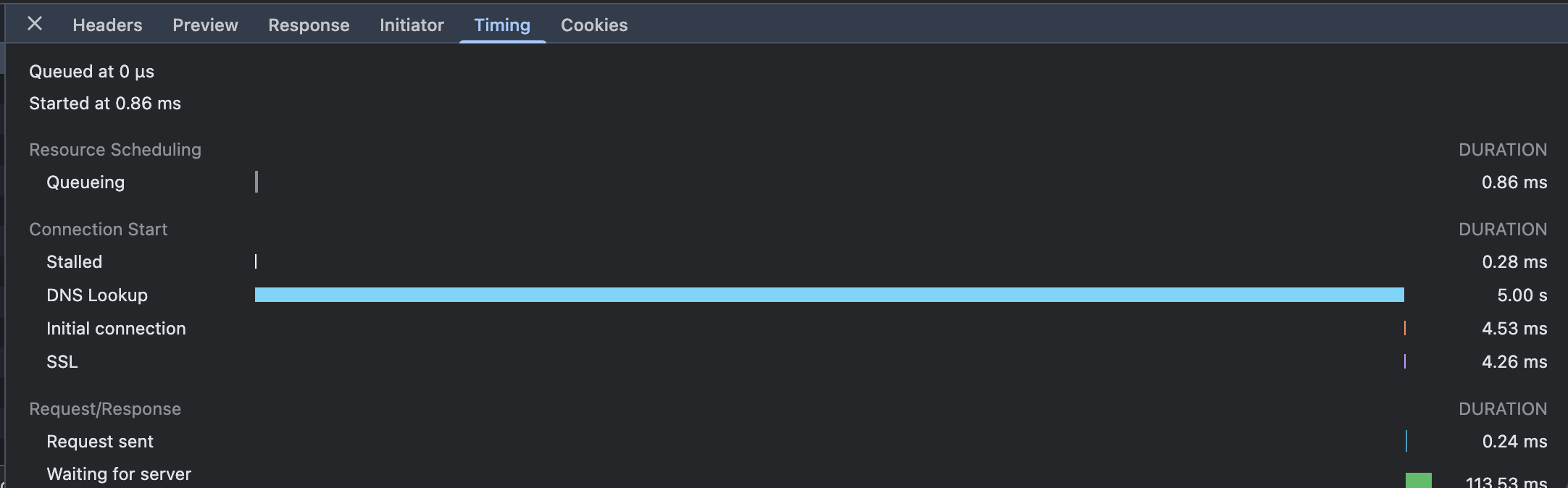 (Screenshot: Viewing DNS Lookup timing in Chrome DevTools Network tab)
(Screenshot: Viewing DNS Lookup timing in Chrome DevTools Network tab)
Cause of the Issue
MAMP and Laravel Herd forcefully modify macOS’s DNS settings during installation by creating special DNS resolver configuration files to hijack certain domain suffixes (such as *.test, *.local). These config files are usually located in /etc/resolver/.
Even after uninstalling MAMP or Herd, these DNS resolver files may remain on your system. When you visit websites using these suffixes (e.g., .test), macOS first tries DNS queries through these outdated resolvers. Since the MAMP/Herd DNS service no longer exists, DNS resolution times out (typically after 5 seconds), then falls back to the system’s default DNS.
Solution
Follow these steps to completely remove DNS configurations left behind by MAMP or Laravel Herd:
1. Properly Uninstall MAMP or Laravel Herd
If you haven’t fully uninstalled MAMP or Laravel Herd, use their official uninstallers or provided scripts:
Uninstalling MAMP:
- Use the built-in uninstaller in the MAMP application
- Or manually delete
/Applications/MAMPand related config files
Uninstalling Laravel Herd:
bash
# Run Herd’s uninstall command
herd uninstall
# If unavailable, manually remove Herd app and config files
rm -rf ~/Library/Application\ Support/Herd
rm -rf ~/.config/herd1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
2. Delete Remaining Files in the /etc/resolver Directory
Even after proper uninstallation, files may linger in /etc/resolver/. Remove these manually:
bash
# List files in /etc/resolver
ls -la /etc/resolver
# Delete specific resolver configs (e.g., test and local)
sudo rm /etc/resolver/test
sudo rm /etc/resolver/local
# Also remove any other resolver files created by MAMP/Herd
# e.g. sudo rm /etc/resolver/herd1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Typical resolver files created by MAMP/Herd:
test— For*.testdomainslocal— For*.localdomainsherd— Laravel Herd specific
Note: Removing these files requires administrator privileges (sudo).
3. Avoid Using *.local Domain Suffixes
macOS reserves the *.local domain suffix for local network (LAN) mDNS (Multicast DNS, aka Bonjour) services. Using .local for local development can cause:
- DNS conflicts
- Slow site access
- Unpredictable network behavior
Suggestion: Use different domain suffixes for local development, such as:
.test— Reserved for testing purposes.localhost— Always resolves to the loopback address.dev— While a real TLD, it’s often used for local development- Or use a custom suffix recommended by ServBay
4. Clear DNS Cache (Optional)
After performing the steps above, clear your system’s DNS cache to ensure changes take effect:
bash
# For macOS Big Sur (11+) and newer
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
# For macOS Catalina (10.15) and earlier
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
5. Verify the Fix
After cleanup, revisit your ServBay site:
- Access your local site in a browser
- Open Chrome DevTools → Network tab
- Refresh and check request Timing
- Confirm DNS Lookup time is now less than 50ms (typically)
These steps should resolve slow initial visits after migrating from MAMP/Laravel Herd. If slowdowns persist, check for interference from third-party software (e.g., VPNs, proxy tools) affecting DNS resolution.
Check Web Server Configuration Files
Errors in web server configuration files are a common cause of site inaccessibility. ServBay provides syntax checking tools for each web server.
Checking the Caddyfile
Use Caddy’s built-in validate command to verify your Caddyfile configuration.
bash
# macOS
/Applications/ServBay/bin/caddy validate -c /Applications/ServBay/etc/caddy/Caddyfile
# Windows
C:\ServBay\bin\caddy.exe validate -c C:\ServBay\etc\caddy\Caddyfile1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
If the syntax is correct, the command returns Valid configuration. If errors exist, you’ll get guidance based on the error type.
Note: The caddy validate command may output many INFO or WARN messages—these are usually informational and not actual config errors. As long as you see Valid configuration at the end, your syntax is fine.
Common Caddyfile Error Examples
Certificate File Not Found:
bash# macOS example 2024/12/09 17:24:16.970 INFO using config from file {"file": "/Applications/ServBay/etc/caddy/Caddyfile"} ... (other INFO/WARN messages) ... Error: loading http app module: provision http: getting tls app: loading tls app module: provision tls: loading certificates: open /Applications/ServBay/ssl/private/tls-certs/mail.servbay.host/mail.servbay.host.1crt: no such file or directory # Windows example 2024/12/09 17:24:16.970 INFO using config from file {"file": "C:\\ServBay\\etc\\caddy\\Caddyfile"} ... (other INFO/WARN messages) ... Error: loading http app module: provision http: getting tls app: loading tls app module: provision tls: loading certificates: open C:\\ServBay\\ssl\\private\\tls-certs\\mail.servbay.host\\mail.servbay.host.1crt: no such file or directory1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9Error messages like
loading certificates: open xxxxx: no such file or directoryindicate the SSL certificate path in your Caddyfile is incorrect or the file doesn't exist. Check your site’s config to ensure certificate (.crt/.cer/.pem) and private key (.key) paths are correct and files exist. ServBay supports manual import or ACME auto-requested SSL certificates—check your ServBay SSL settings as needed.Website Root Directory Path Error (contains spaces):
bash# macOS example 2024/12/09 17:26:37.371 INFO using config from file {"file": "/Applications/ServBay/etc/caddy/Caddyfile"} Error: adapting config using caddyfile: parsing caddyfile tokens for 'root': too many arguments; should only be a matcher and a path, at /Applications/ServBay/etc/caddy/Caddyfile:1388 # Windows example 2024/12/09 17:26:37.371 INFO using config from file {"file": "C:\\ServBay\\etc\\caddy\\Caddyfile"} Error: adapting config using caddyfile: parsing caddyfile tokens for 'root': too many arguments; should only be a matcher and a path, at C:\\ServBay\\etc\\caddy\\Caddyfile:13881
2
3
4
5
6
7This error,
parsing caddyfile tokens for 'root': too many arguments, is usually caused by spaces in the site root directory path. For example:- macOS:
root * /Applications/ServBay/www/public web– herepublic webis interpreted as two arguments - Windows:
root * C:\ServBay\www\public web– same issue
Correct way: Wrap paths containing spaces in double quotes
":- macOS:
root * "/Applications/ServBay/www/public web" - Windows:
root * "C:\ServBay\www\public web"
Tip: To avoid such issues, use hyphens (
-) or underscores (_) instead of spaces or special characters—e.g.,public-folderorpublic_dir.- macOS:
Rewrite Rule Errors:
Copy-pasting incompatible NGINX rewrite rules into a Caddyfile will cause validation failures. Always consult Caddy rewrite docs and ServBay’s NGINX-to-ServBay migration guide to ensure correct syntax.
NGINX Configuration Checks
Use NGINX’s built-in -t flag to test config syntax and validity.
bash
# macOS
/Applications/ServBay/bin/nginx -t
# Windows
C:\ServBay\bin\nginx.exe -t1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
With correct config, you'll see:
# macOS
nginx: the configuration file /Applications/ServBay/etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /Applications/ServBay/etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
# Windows
nginx: the configuration file C:\ServBay\etc\nginx\nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file C:\ServBay\etc\nginx\nginx.conf test is successful1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
If there are errors, NGINX will point out the problematic file and line. Common issues include:
- Syntax errors: Missing semicolons
;, unmatched braces}. - File path errors: Specified in
includeor other directives. - Port conflicts: The port being listened to is occupied.
Apache Configuration Checks
Use Apache’s apachectl configtest to validate configuration syntax.
bash
# macOS
/Applications/ServBay/bin/apachectl configtest
# Windows
C:\ServBay\bin\httpd.exe -t1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
If the config is valid, you'll see Syntax OK; otherwise, detailed error info is shown. Common issues include:
- Module load failures:
LoadModulemodules not found or path errors. - .htaccess syntax errors: Mistakes in
.htaccessfiles can break config or cause directory-specific errors. - Incorrect directory permission settings:
Directory,Filesdirectives’ permissions (Require,Allow,Deny) blocking file access.
Handling 500 Internal Server Errors
The 500 Internal Server Error means that the server encountered an unexpected condition, unable to fulfill the request. In web apps, this usually points to failed backend scripts (e.g., PHP, Python, Node.js).
General Troubleshooting Steps
When you encounter a 500 error, try these steps:
Check Web Server Error Logs: This is the first thing to do. Error logs contain details about script issues, missing files, permission problems, etc.
macOS:
- Caddy:
/Applications/ServBay/var/logs/caddy/error.log - NGINX:
/Applications/ServBay/var/logs/nginx/error.log - Apache:
/Applications/ServBay/var/logs/apache/error.log
Windows:
- Caddy:
C:\ServBay\var\logs\caddy\error.log - NGINX:
C:\ServBay\var\logs\nginx\error.log - Apache:
C:\ServBay\var\logs\apache\error.log
Review the latest entries, looking for
errororcriticalkeywords.- Caddy:
Check if Backend Services (e.g., PHP-FPM) Are Running: If your site relies on PHP, ensure PHP-FPM is running.
bashps aux | grep php-fpm1Look for
php-fpm: master processorphp-fpm: pool www. If not present, PHP-FPM is not started or has crashed. Start PHP from the ServBay UI or viaservbayctl.Check Backend Script (PHP) Error Logs: If the web server log points to FastCGI or backend errors, inspect the backend language logs.
PHP error log locations:
- macOS:
/Applications/ServBay/var/logs/php/php_error.log - Windows:
C:\ServBay\var\logs\php\php_error.log
Look for
Fatal error,Parse error,Warning, orNoticeentries, especially those related to your scripts. In dev environments, you may enabledisplay_errorsfor diagnostic details (set inphp.ini), but keep it off in production.- macOS:
Check File and Directory Permissions: Web server processes run under a specific user and need sufficient permissions for site files, upload folders, and logs.
macOS:
bashls -la /Applications/ServBay/www/your-site/1Ensure the web server user (e.g.,
_www) has read (and, where needed, write) access. Alter permissions/ownership usingchmod/chown.Windows:
cmddir C:\ServBay\www\your-site1Check that the ServBay user account has proper directory permissions via the Security tab in file properties.
500 Error Troubleshooting by Web Server
Caddy:
- FastCGI settings: Ensure the
php_fastcgiorreverse_proxyin Caddyfile points to PHP-FPM’s address (typically127.0.0.1:9000orunix:/path/to/php-fpm.sock). - PHP-FPM status: Confirm the relevant PHP version and PHP-FPM services are running in ServBay.
- Reverse proxy config: If using
reverse_proxyto backend services (e.g., Node.js), ensure the proxy host/port is correct and that the backend is up.
- FastCGI settings: Ensure the
NGINX:
fastcgi_passsettings: Check thatfastcgi_passinnginx.confor site configs correctly targets PHP-FPM.client_max_body_size: Set this higher if large uploads trigger 500 errors.try_filesdirective: Confirm its config so requests go to the proper index or FastCGI handler.
Apache:
mod_rewritemodule: If using.htaccessfor URL rewriting, confirmmod_rewriteis present.- .htaccess content: Syntax errors in
.htaccesscan trigger 500 errors; check those rules carefully. AllowOverridesettings: In Apache config, ensure relevant directories haveAllowOverrideset toAllor at leastFileInfoandLimitso.htaccessrules are effective.
Service Management
Most changes to configs or backends require restarting web servers or services.
Restart Services
Use servbayctl restart to restart web server services:
bash
# Restart Caddy
servbayctl restart caddy -all
# Restart NGINX
servbayctl restart nginx -all
# Restart Apache
servbayctl restart apache -all1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
The -all flag will also attempt to restart supporting services like PHP-FPM.
Check Service Status
Use servbayctl status to view service status:
bash
# Check Caddy status
servbayctl status caddy -all
# Check NGINX status
servbayctl status nginx -all
# Check Apache status
servbayctl status apache -all1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Output shows if services are running, stopped, or other states—helpful for service verification.
Advanced Troubleshooting Steps
If the above haven’t solved your problem, try these deeper checks:
- Inspect browser DevTools: Open DevTools (usually F12), look at the
ConsoleandNetworktabs. Check for front-end JS errors and detailed HTTP status codes to distinguish frontend vs backend issues. - Use
curl -v: Runcurl -v your-website.servbay.demoin the terminal, replacing with your actual site. The-vflag shows detailed request/response, including headers and TLS info, helpful for diagnosing connection or protocol issues. - Temporarily disable firewalls: Local firewalls (e.g., macOS’s built-in) or security software may block incoming connections. Try disabling them; if that fixes it, re-enable and properly allow ServBay’s ports (80, 443, etc.).
- Test with other browsers/devices: Access your site from various browsers or a different device to rule out browser cache or device-specific configs.
- Check local DNS or hosts file: For custom domains (not
localhost/IP), inspect your hosts file or local DNS to ensure the domain maps to127.0.0.1or::1.- macOS:
/etc/hosts - Windows:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
- macOS:
Conclusion
Web server troubles are a common part of local development. By methodically checking configuration syntax, reviewing error logs, confirming service states, and verifying permissions, most issues can be resolved. ServBay’s built-in troubleshooting tool and servbayctl CLI are valuable aids. For complex problems, don’t hesitate to consult ServBay’s documentation or contact their technical support team for assistance.

